What is Piling?
6 min read
A pile is basically a long cylinder of a strong material such as concrete that is pushed into the ground to act as a steady support for structures built on top of it.
Pile foundations are used in the following situations:
When there is a layer of weak soil at the surface. This layer cannot support the weight of the building, so the loads of the building have to bypass this layer and be transferred to the layer of stronger soil or rock that is below the weak layer.
When a building has very heavy, concentrated loads, such as in a high rise structure, bridge, or water tank.
Pile foundations are capable of taking higher loads than spread footings.
There are two fundamental types of pile foundations (based on structural behaviour), each of which works in its own way.
- End Bearing Piles
In end bearing piles, the bottom end of the pile rests on a layer of especially strong soil or rock. The load of the building is transferred through the pile onto the strong layer. In a sense, this pile acts like a column. The key principle is that the bottom end rests on the surface which is the intersection of a weak and strong layer. The load therefore bypasses the weak layer and is safely transferred to the strong layer.
Basically, there are 5 types of end Bearing Piles which are:
a. Bored Piling
Installed by auguring into the ground forming a hole into which concrete can be poured, thereby casting the pile in position. This method of piling is well suited for work in cities and areas surrounding existing buildings as the vibration caused by installation is minimised.
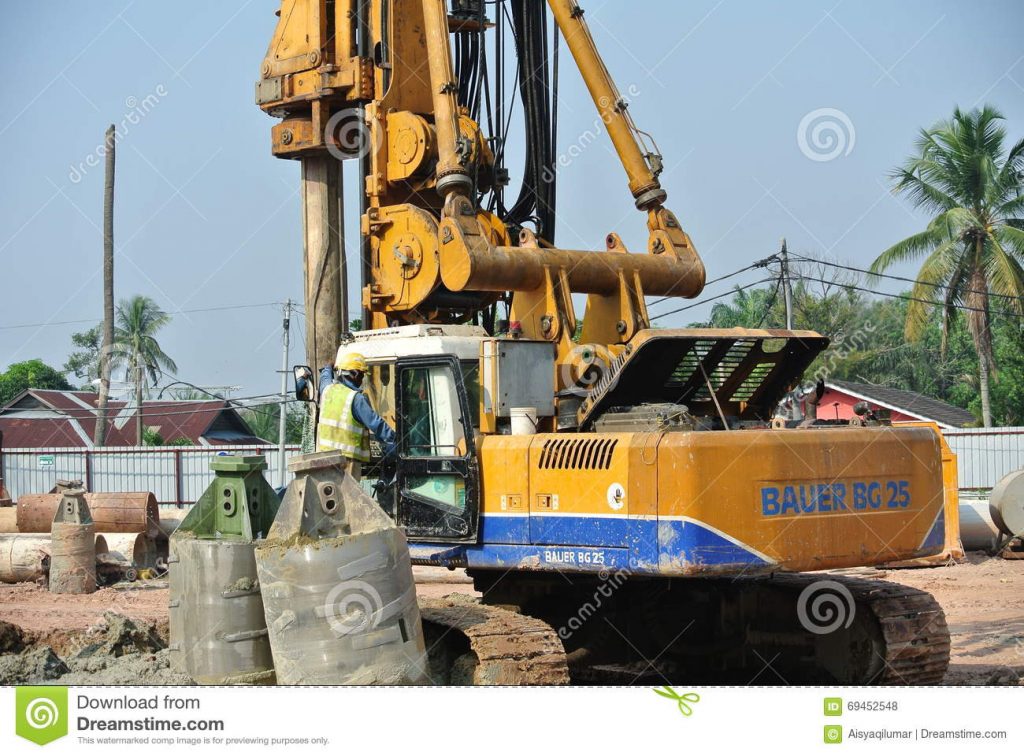

An open bored pile is constructed by boring into the ground and removing the augur stem forming an open hole into which steel and concrete can be installed, which is suitable for cohesive ground with low water tables. When a pile is augured and the concrete is poured before the augers are extracted it is referred to as a CFA pile (continuous flight auger) or SFA pile (sectional flight auger).
b. Driven Piling
Driven piles are driven or hammered into the ground with the use of vibration. This method of piling is well suited for foundations in non-cohesive soils, ground with a high water table and for soils that contain contaminates.
Driven piles can be cast in position by using temporary or permanent steel casing. They can also be prepared off site by using pre-cast piles, which can be created using steel, timer, wood, concrete or a combination of these.

c. Screw Piling
Screw piles use circular hollow galvanised steel pile shafts with one or more steel helices attached to them and are fastened into the ground much like a screw is fastened into wood.
This type of pile minimises the spoil created by installation and in some instances may provide a more sustainable and cost effective alternative to other methods.

d. Sheet Piling
Sheet piles, a type of driven pile, are constructed with a series of interlocking steel sheets. They can be used to create permanent or temporary retaining walls on construction sites where large excavations are required.
This method of piling can be very cost effective on sites where temporary soil retention is necessary as the sheets can removed and used again on different sites once the ground works have been completed.

e. Mini Piling
Mini piles, also known as micro piles, typically range in sizes from 100 mm – 400 mm in diameter. What distinguishes mini piles from other pile types, however, has more to do with how and where they are installed than just the pile size itself.
In locations with restricted access smaller sized piling rigs have been required in order to install piles on sites where traditional piling rigs could not operate. This opens up many options for commercial & domestic development in the city.

- Friction Piles
Friction piles work on a different principle. The pile transfers the load of the building to the soil across the full height of the pile, by friction. In other words, the entire surface of the pile, which is cylindrical in shape, works to transfer the forces to the soil.
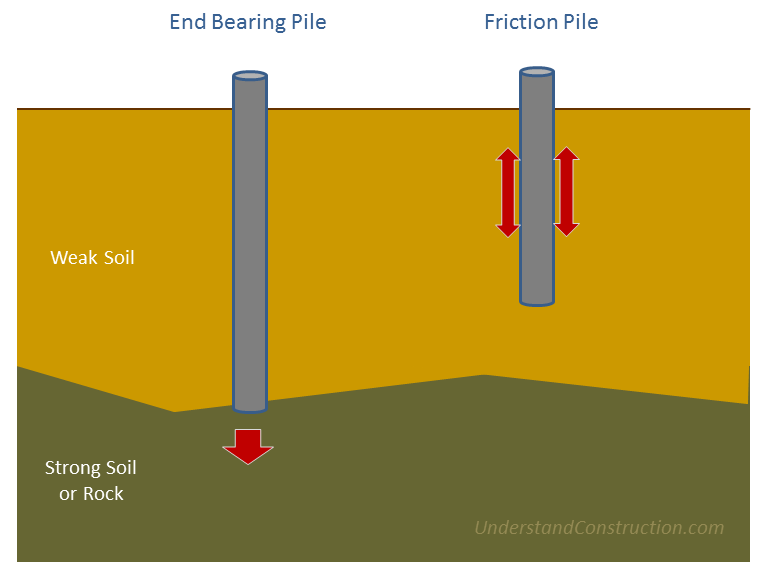
To visualise how this works, imagine you are pushing a solid metal rod of say 4mm diameter into a tub of frozen ice cream. Once you have pushed it in, it is strong enough to support some load. The greater the embedment depth in the ice cream, the more load it can support. This is very similar to how a friction pile works. In a friction pile, the amount of load a pile can support is directly proportionate to its length.
WHAT ARE PILES MADE OF?
Piles can be made of wood, concrete, or steel.
In traditional construction, wooden piles were used to support buildings in areas with weak soil. Wood piles are still used to make jetties. For this one needs trees with exceptionally straight trunks. The pile length is limited to the length of a single tree, about 20m, since one cannot join together two tree trunks. The entire city of Venice in Italy is famous for being built on wooden piles over the sea water.
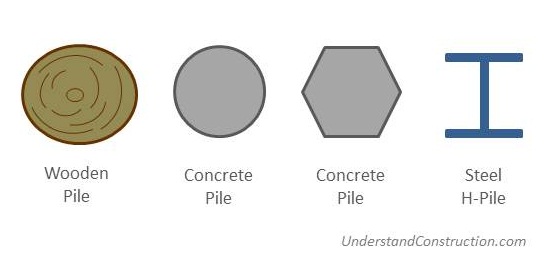
Concrete piles are precast, that is, made at ground level, and then driven into the ground by hammering – more on that later. Steel H-piles can also be driven into the ground. These can take very heavy loads, and save time during construction, as the pile casting process is eliminated. No protective coating is given to the steel, as during driving, this would be scraped away by the soil. In areas with corrosive soil, concrete piles should be used.
HOW PILES ARE USED
As pile foundations carry a lot of load, they must be designed very carefully. A good engineer will study the soil the piles are placed in to ensure that the soil is not overloaded beyond its bearing capacity.
Every pile has a zone of influence on the soil around it. Care must be taken to space the piles far enough apart so that loads are distributed evenly over the entire bulb of soil that carries them, and not concentrated into a few areas.
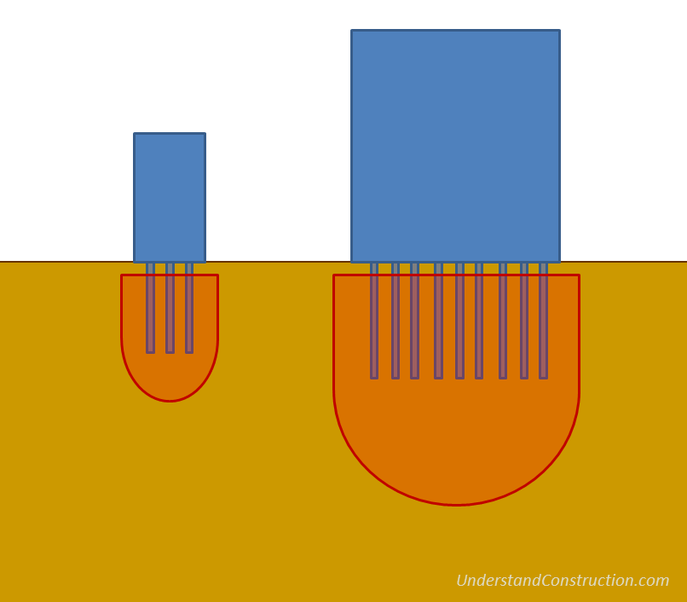
Engineers will usually group a few piles together, and top them with a pile cap. A pile cap is a very thick cap of concrete that extends over a small group of piles, and serves as a base on which a column can be constructed. The load of this column is then distributed to all the piles in the group.
HOW PILES ARE CONSTRUCTED
Piles should be hammered into the ground till refusal, at which point they cannot be driven any further into the soil.
SPECIAL PILES
Pile driving is very noisy and causes massive vibrations through the soil. For this reason, it is sometimes difficult to use them in sensitive locations. For example, if an operational hospital or science lab is to be extended, driving piles would cause unwanted disturbance. Their use is also restricted in residential areas in many countries. The vibrations could also cause structural damage to older buildings that are close by. In such situations it is possible to use micropiling or helical piling, neither of which rely on hammering.
Micropiles or minipiles are small piles that are constructed in the following way:
Step 1: a hole a little larger than the pile diameter and the full length of the pile is dug into the ground using an apparatus like a soil boring machine.
Step 2: a precast concrete pile is lowered or pushed into the hole.
Step 3: a concrete grout is poured into the gap between the pile and the earth.
Helical piles are steel tubes that have helical (spiral) blades attached to them. These can be drilled into the ground, meaning that the pile acts as a giant drill bit, and is rotated and pushed into the ground from above, much like a screw drills into wood. Once the steel pile is driven into the ground, a pile cap is poured on top of the pile to prepare it for the construction above.
Please keep in touch to know more about us and please do not hesitate to contact us for your next piling job.



